| ✅ Reviewed by Dr. Tom McCawley | 🕒 Reading time: four minutes |
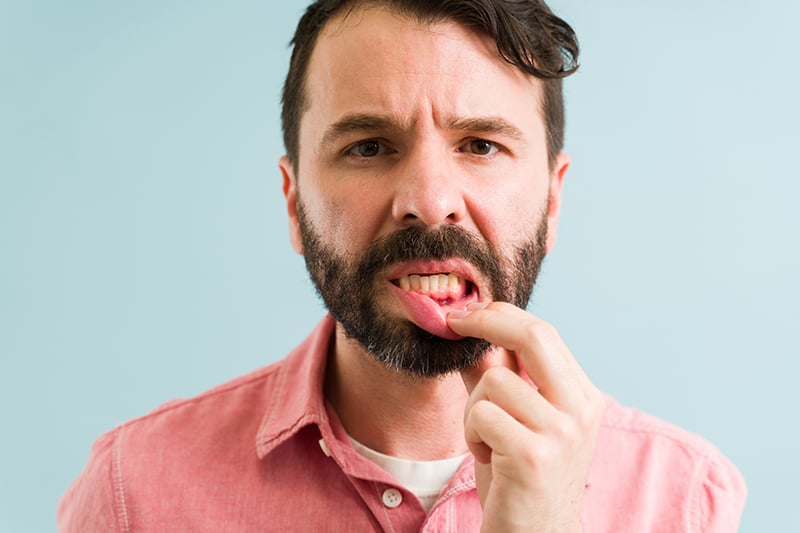
Gum disease is one of the most common oral health conditions in adults and one of the most misunderstood. A question that often arises is whether it can be passed from one person to another. The short answer: yes but there’s more to the story.
In this blog, we will answer a common concern: Is gum disease contagious or transmissible? You will learn how the bacteria behind gum infections are transmitted, what increases your risk, and how daily habits and professional care can help protect both your oral and overall health.
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also called periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection that damages the soft tissue and bone supporting your teeth.
It begins with plaque buildup, a sticky film of bacteria that collects around the gum tissue. Gingivitis, the earliest form of gum disease, causes inflammation and bleeding but can often be reversed with proper home care and professional cleanings. If left untreated, it can progress to more serious stages that threaten your teeth and overall health.
Learn more about Gum Disease.
| ⚠️ Gum Disease Affects More Than Just Your Mouth When gum infections go untreated, the bacteria can enter your bloodstream and contribute to inflammation throughout the body. Research has linked advanced periodontal disease to serious health issues, including heart disease, diabetes complications, and even stroke. Protecting your oral health with regular brushing, dental cleanings, and early treatment helps preserve your teeth and plays an important role in supporting your overall well-being. |
The Stages of Gum Disease
Periodontal disease progresses in stages. Understanding where you are in this progression is key to getting the right treatment.
- Gingivitis: The earliest stage, marked by red, swollen gums that may bleed. At this point, damage is still reversible with brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings.
- Periodontitis: When left untreated, the infection moves deeper, forming periodontal pockets and attacking the bone and connective tissues that anchor your teeth. Treatment often involves root planing or laser therapy to remove harmful bacteria.
- Advanced Periodontitis: This stage can result in significant bone loss, gum recession, loose teeth, and eventual tooth loss.
Can It Be Spread From Person to Person?
The bacteria responsible for periodontal disease can be transferred through saliva contact. Activities like kissing, sharing utensils, or using someone else’s toothbrush can expose you to the same harmful bacteria that cause gum infections.
You get the bacteria that cause periodontal disease from four primary sources: your parents, your significant others, your pets or travel to third world countries where the water is contaminated.
Does That Mean You’ll Get Gum Disease If Exposed?
Transmitting bacteria is only one part of the puzzle. Whether you develop gum disease depends on several factors, including:
- Daily oral hygiene habits
- Frequency of professional cleanings
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Health conditions like diabetes
- Genetics
- The strength of your immune response
If your oral hygiene is consistent and your gums are healthy, your body can usually keep bacterial exposure in check.
| 📌 What Increases Your Risk of Gum Disease? Some people are simply more prone to gum problems than others. If you smoke, have diabetes, deal with high stress, or take medications that cause dry mouth, your gums may need extra attention. Even genetics and hormone changes can play a role. The good news? With regular home care, consistent dental cleanings, and early care when needed, you can stay ahead of it. |
When the Risk Is Higher
If your gums are already inflamed or you are in a stage of gum disease, exposure to additional bacteria, especially from someone with active periodontal disease, can worsen the condition or make treatment more difficult.
Deep pockets around the teeth create ideal environments for bacteria to thrive, and once infection reaches the tooth roots and supporting bone, the stakes rise.
How to Protect Your Oral Health
Daily habits play a major role in preventing periodontal disease, even if you have been exposed to harmful bacteria. A consistent routine paired with professional care can go a long way in protecting your gums, teeth, and overall health.
- Practice regular brushing and flossing and often water piking. Removing plaque every day helps prevent it from hardening into tartar and triggering infection.
- Stay on schedule with dental cleanings and exams. Professional care removes buildup you can’t reach at home and allows early detection of any issues.
- Avoid sharing oral items. This includes drinks, utensils, straws, and toothbrushes, all of which can transfer bacteria.
- Know the signs of infection. Watch for bleeding gums, gum recession, persistent bad breath, or loose teeth.
- Don’t delay treatment. If you or your partner has gum disease, early intervention antimicrobial therapy and LANAP® can help preserve healthy tissue and prevent tooth loss.
The Bottom Line
The bacteria that cause gum disease can be passed between people. Good oral hygiene, regular dental care, and early treatment are your best defense, whether you’re trying to prevent infection or manage an existing condition.
Book a Consultation in Fort Lauderdale
If you have noticed signs of gum infection or want to better protect your smile, we can help. At the McCawley Center for Laser Periodontics & Implants, we focus on treating the bacterial source of periodontal disease to preserve your natural teeth and improve your overall health.
To book an appointment at our periodontal office in Fort Lauderdale, FL, call (954) 807-4829 or visit us at 800 East Broward Blvd #706 Fort Lauderdale, FL.